On the Utilized Programs Group within the SEI’s CERT Division, one among our areas of labor focuses on Docker container photos that require hardening to take away vulnerabilities. By way of our work, we’ve seen stakeholders encountering problem with hardening open-source container photos, along with creating routine processes for vulnerability mitigation for Docker container photos.
Utilizing unvetted container photos can improve safety dangers by way of the introduction of weak software program into a corporation’s software program provide chain. For instance, unvetted container photos may include packages with recognized Widespread Vulnerabilities and Exposures (CVEs), introducing a possible exploitation vector. As this weblog submit particulars, hardening these container photos, or choosing verified pre-hardened container photos earlier than utilization, decreases the danger of introducing weak software program.
Hardening containers and container photos entails analyzing their present safety standing after which making use of remediations to iteratively enhance safety. The hardening course of is routine and offers iterative safety monitoring throughout the improvement course of. A hardened picture offers a safe sandbox for improvement and execution of open-source software program.
The Container Hardening Course of
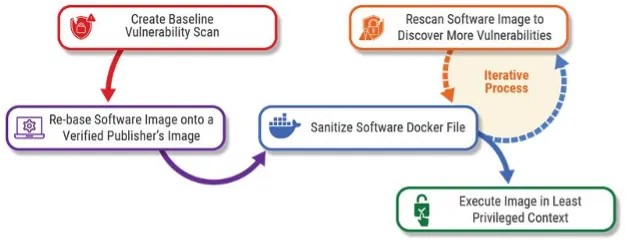
Determine 1: The iterative container hardening course of for vulnerability detection and remediation.
The method of hardening containers and container photos begins with a baseline safety scan of the unhardened picture to create a listing of recognized vulnerabilities. As soon as this baseline has been made, engineers ought to analyze the picture Dockerfile and exchange any non-standard base photos with respected base photos from verified publishers. Following the rebasing, engineers, utilizing container picture options similar to Docker, ought to start the iterative course of to remediate recognized bugs whereas scanning for brand new vulnerabilities.
It is advisable to exchange non-standard photos utilized in a Dockerfile as a result of, as we talked about earlier, photos can convey vulnerabilities that may discover their manner into the tip product. This may take the type of weak packages or different dependencies utilized by the picture, however it could possibly additionally come because of unsecure practices within the picture itself. To counteract this, rebasing the Dockerfile to make use of photos from Docker verified publishers similar to Pink Hat permits for extra stability in updates and vulnerability mitigation.
These ways of scanning and substituting photos is actually the beginnings of a software program invoice of supplies (SBOM), and this makes it simpler to create and monitor an SBOM. The outputs of every safety scan assist establish the place actions are wanted when new vulnerabilities come to gentle and could be added to the SBOM to keep up its accuracy.
Decreasing Potential Vulnerabilities in Container Photographs
A number of different practices may also be employed when rebasing a Dockerfile to additional mitigate dangers and vulnerabilities. For starters, if a Dockerfile doesn’t make use of it already, engineers can implement a multi-stage construct course of. This permits the construct course of to put in the dependencies wanted to construct elements of the service, whereas leaving these construct dependencies behind of their respective levels. Doing this enables the construct course of to convey solely what’s required for the ultimate picture into the ultimate construct stage. Leaving these runtime-irrelevant dependencies out of the ultimate picture can scale back the picture’s risk floor.
In the identical vein, a extra minimal base picture may also be useful. Constructing a container to serve a database, for instance, is unlikely to want a lot of the options of a full working system (OS) base picture. A number of frequent base photos similar to Pink Hat Common Base Picture(UBI), Debian, and Rocky Linux provide stripped-down variations leaving fewer superfluous and doubtlessly weak packages and configurations, and in addition provides the additional benefit of decreasing the dimensions of the ultimate picture. For extra on the subject of decreasing the dimensions of photos, try this SEI presentation by Kevin Pitstick.
There are just a few different tweaks that may additionally support in decreasing potential vulnerabilities in container photos. Certainly one of these is to exchange using the ADD instruction with the COPY instruction wherever doable. ADD and COPY overlap in that they’ll each be used to maneuver native information round throughout the picture constructing course of. Nevertheless, ADD has the extra functionality of with the ability to obtain information referenced by exterior URLs, in addition to unpackage archives. These further capabilities could be undesirable additions when safety is a priority. Containers also needs to be set to run as a non-root service consumer when doable, to restrict their potential to carry out malicious duties if compromised. Notice that by default, Docker containers run as root. By working a container as a non-root service, the precept of least privilege is adopted. It’s additionally a superb apply to outline the service consumer early on in a Dockerfile, switching again to root solely as wanted within the construct course of.
The Significance of Vulnerability Scanning
Vulnerability scanning is a vital step in figuring out vulnerabilities in a container picture. Utilizing instruments similar to Grype and Trivy, safety and infrastructure engineers can routinely run safety scans on open-source photos along with photos constructed through an automatic pipeline. Creating an automatic course of to routinely scan the container picture is a typical a part of most DevSecOps pipelines and can add larger visibility into vulnerability detection. Routine scanning additionally permits for the institution of a vulnerability baseline and incremental mitigation.
Vulnerability scans sometimes yield a listing of CVEs, which include details about the vulnerability and any potential mitigations. A CVE normally has a Widespread Vulnerability Scoring System (CVSS) rating, which assesses the severity of the vulnerability. Calculating or wanting up the CVSS rating can streamline the method of prioritizing the remediation of vulnerabilities.
Hardening of Docker photos entails inspection of how the picture is constructed, routinely scanning the constructed picture for vulnerabilities, after which making use of mitigations to the picture constructing course of. The continual means of scanning new revealed photos helps detect any new vulnerabilities. By establishing a routine course of for hardening photos, confidence is gained within the manufacturing pipeline ranging from the event stage.