The newest Annual Cybersecurity Attitudes and Behaviours Report, launched by way of the Australian Cyber Collaboration Centre, has published each Australian and international workforces are showing quite a lot of regarding cybersecurity behaviours, together with important tendency to percentage corporate information with AI equipment.
Surveying 6,500 folks of various ages in 8 nations, together with Australia and New Zealand, the record discovered IT and cybersecurity leaders are making headway towards making improvements to safety by way of cybersecurity coaching. However, they’re nonetheless fighting a number of deficient cybersecurity attitudes and behaviours of their workforces that might obstruct this growth.
Cybersecurity is exasperating to many people and staff
The record discovered that Australians, like others around the globe, are more and more annoyed by way of the will for consistent on-line cybersecurity measures. In an Australian cybersecurity atmosphere that has integrated pervasive digitisation of industrial and services and products, in addition to a huge selection of information breaches:
- 52% of respondents reported that on-line safety is “frustrating” for them, with 44% admitting they really feel intimidated by way of the complexities of staying protected on-line.
- There has been an important decline within the perceived worth of on-line safety, with most effective 60% of Australians believing it’s definitely worth the effort, a drop of 9% since closing yr.
- Gen Z and Millennials are essentially the most pessimistic about their talent to stick protected on-line, with many having lowered their on-line actions because of those considerations.
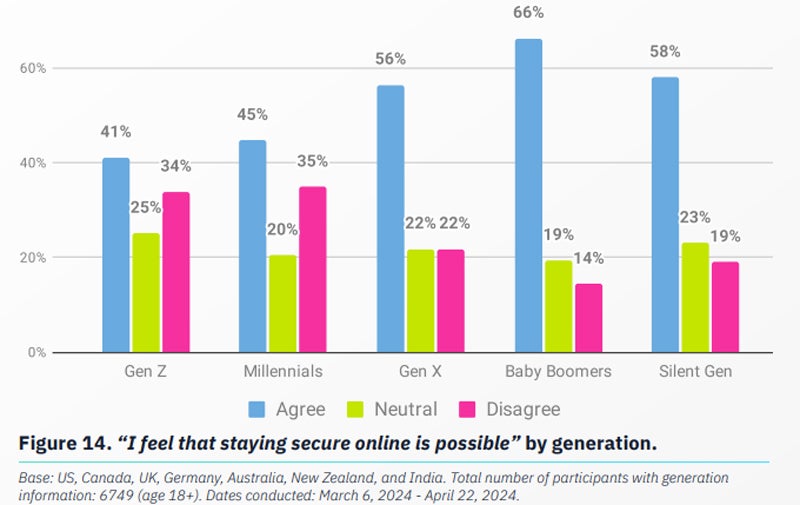
The effects recommend a emerging discontent with the downsides of the virtual atmosphere during which folks paintings. The complexities and friction of navigating cybersecurity to minimise dangers might be inflicting disengagement with safety practices, which might threaten employer information security features.
SEE: APAC staff are opting for comfort, velocity over cybersecurity
Individuals are outsourcing accountability for cybersecurity
Individuals more and more be expecting others to be answerable for the safety in their data, together with the tech business and tech platforms. In Australia, 90% of contributors throughout all age teams imagine apps and platforms must be answerable for protective their private data. In addition:
- IT and safety departments are seen as maximum answerable for safeguarding data within the place of work, although extra staff now characteristic extra accountability to the tech business.
- The share of people who view themselves as basically answerable for safety dropped by way of 7% from 2023.
- The Australian Cyber Collaboration Centre discovered “widespread complacency,” with 43% assuming their units had been mechanically safe. That share was once upper for more youthful generations.
Premium: How to create a cybersecurity consciousness program
“Complacency and frustration are dangerous combinations in the fight against cybercrime in Australia,” Matthew Salier, leader govt officer on the Australian Cyber Collaboration Centre, mentioned in a commentary. “Vulnerability to cyber-attacks is of particular concern across younger generations because they’re not taking adequate precautions, relying too heavily on others or assuming their devices are secure.”
Key cybersecurity behaviours nonetheless have room for development
The record discovered folks nonetheless fight with keeping up cybersecurity hygiene, which might affect employers:
Password utilization: The use of private data for passwords, corresponding to members of the family or puppy names, rose throughout all generations, with Gen Z the crowd perhaps to make use of those passwords (52%). The maximum most well-liked approach for managing passwords amongst the ones with a couple of on-line account is to put in writing them down in a bodily pocket book (29%), whilst simply 12% use a password supervisor.
Multi-factor authentication: An enormous 81% of respondents have heard of MFA, up 11% on closing yr, which must assist cybersecurity execs enforcing the era. However, adoption is inconsistent. The record discovered MMA adoption might be irritating for the person enjoy, with many more youthful customers who’ve attempted to put into effect MFA prior to now on their units having since deserted it.
Phishing detection: The survey contributors had been in a position to recognise phishing emails or malicious hyperlinks, with 67% throughout geographies announcing they felt assured they might accomplish that. However, 10% of respondents mentioned they weren’t assured. The record urged this was once as a result of the expanding sophistication of phishing makes an attempt, together with criminals the usage of AI.
Over part of staff haven’t won coaching for protected AI use
Artificial intelligence equipment are growing new cybersecurity and knowledge safety problems within the place of work:
- In Australia, greater than part of hired contributors (52%) have no longer but won any coaching on protected AI use, regardless of considerations corresponding to information leakage and over-reliance on responses.
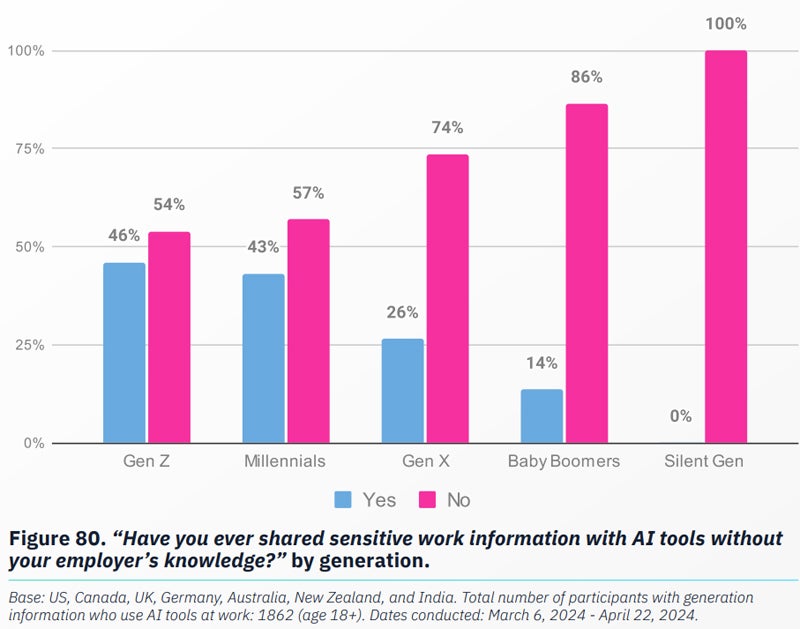
- A stunning 38% of world respondents throughout all jurisdictions surveyed admitted to sharing delicate paintings data with AI with out their employer’s wisdom.
- The occurrence of staff sharing information with AI was once upper amongst more youthful generations, with 46% of Gen Z and 43% of Millennials sharing information with AI, when put next with 26% of Gen Xers.
Organisations no longer depended on to put into effect AI responsibly
There is proof folks will have low accept as true with within the talent of organisations and IT to put into effect AI:
- Trust in firms responsibly enforcing AI was once lowest in Australia, the place simply 35% believed that businesses had been as much as the problem of enforcing AI ethically.
- Millennials in Australia are anxious AI will make detecting scams much more difficult.
Academy: Skill up with our very personal 2024 cybersecurity mastermind coaching package
There are some international considerations that AI will affect jobs. Almost part of Gen Z (48%) and Millennials (49%) felt it was once most likely AI will motive adjustments to their employment standing, although the Baby Boomers and Silent Generation had been much less involved concerning the affect of AI on their paintings (13% and 11%, respectively).
Cybersecurity coaching supplies silver lining for IT execs
Despite the record revealing some regarding cybersecurity behaviours, IT and cybersecurity execs had been given a sign the cybersecurity coaching systems they’ve rolled out seem to be expanding cybersecurity consciousness amongst people who are their staff:
- The majority (83%) of the ones surveyed who accessed coaching at their place of work or position of schooling discovered it helpful.
- The greatest affects reported had been on recognising and reporting phishing messages (52%) and the usage of MFA (45%).
- Overall, the record discovered there have been will increase within the perceived affect of coaching on all safety behaviors when put next with 2023.
“As the threat landscape evolves with the introduction of AI,” Salier concluded, “we must equip individuals and organisations in Australia with the tools they need to navigate this complex environment.”






No Comment! Be the first one.