Discover ways to use UICollectionView, with extremely reusable UIKit parts and a few MVVM sample with out the going nuts with index path calculations.
Anatomy of the UICollectionView class
In the event you’re not aware of UICollectionView, I’d counsel to get aware of this class instantly. They’re the fundamental constructing blocks for a lot of apps offered by Apple and different third occasion builders. It’s like UITableView on steroids. Here’s a fast intro about methods to work with them by IB and Swift code. 💻
You might need seen that I’ve a love for steel music. On this tutorial we’re going to construct an Apple Music catalog like look from floor zero utilizing solely the mighty UICollectionView class. Headers, horizontal and vertical scrolling, round pictures, so principally nearly all the pieces that you just’ll ever must construct nice person interfaces. 🤘🏻
The right way to make a UICollectionView utilizing Interface Builder (IB) in Xcode?
The brief & sincere reply: you shouldn’t use IB!
In the event you nonetheless need to use IB, here’s a actual fast tutorial for completely newbies:
The principle steps of making your first UICollectionView based mostly display screen are these:
- Drag a UICollectionView object to your view controller
- Set correct constraints on the gathering view
- Set dataSource & delegate of the gathering view
- Prototype your cell structure contained in the controller
- Add constraints to your views contained in the cell
- Set prototype cell class & reuse identifier
- Do some coding:
import UIKit
class MyCell: UICollectionViewCell {
@IBOutlet weak var textLabel: UILabel!
}
class ViewController: UIViewController {
@IBOutlet weak var collectionView: UICollectionView!
override func viewDidLayoutSubviews() {
tremendous.viewDidLayoutSubviews()
if let flowLayout = collectionView.collectionViewLayout as? UICollectionViewFlowLayout {
flowLayout.itemSize = CGSize(
width: collectionView.bounds.width,
peak: 120
)
}
}
}
extension ViewController: UICollectionViewDataSource {
func numberOfSections(
in collectionView: UICollectionView
) -> Int {
1
}
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
numberOfItemsInSection part: Int
) -> Int {
10
}
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath
) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(
withReuseIdentifier: "MyCell",
for: indexPath
) as! MyCell
cell.textLabel.textual content = String(indexPath.row + 1)
return cell
}
}
extension ViewController: UICollectionViewDelegate {
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
didSelectItemAt indexPath: IndexPath
) {
print(indexPath.merchandise + 1)
}
}
In a nutshell, the info supply will present all of the required information about methods to populate the gathering view, and the delegate will deal with person occasions, comparable to tapping on a cell. You need to have a transparent understanding in regards to the information supply and delegate strategies, so be happy to play with them for a short time. ⌨️
The right way to setup a UICollectionView based mostly display screen programmatically?
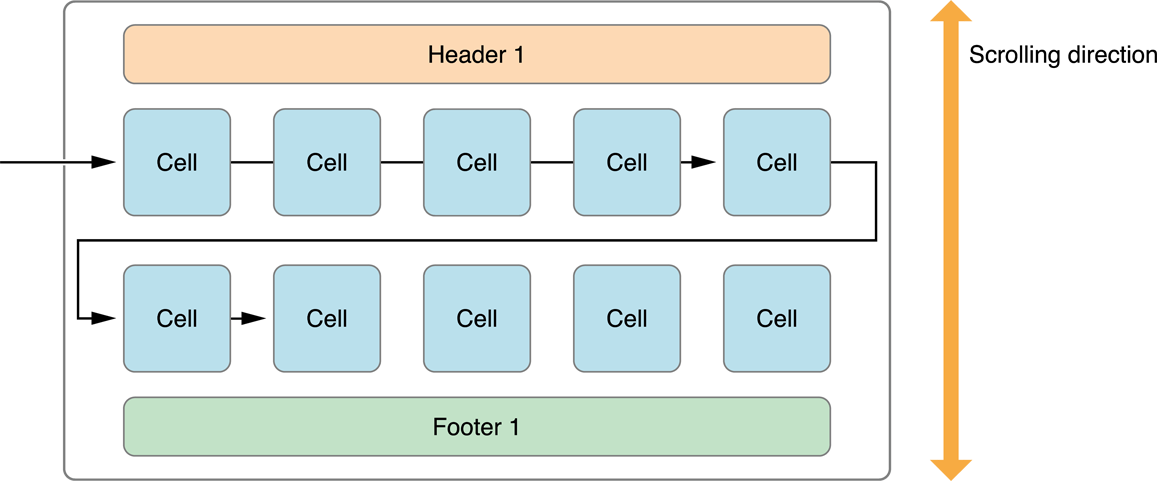
As you might need seen cells are the core parts of a group view. They’re derived from reusable views, because of this if in case you have a listing of 1000 components, there gained’t be a thousand cells created for each aspect, however just a few that fills the scale of the display screen and once you scroll down the record this stuff are going to be reused to show your components. That is solely due to reminiscence issues, so not like UIScrollView the UICollectionView (and UITableView) class is a extremely good and environment friendly one, however that is additionally the explanation why you must put together (reset the contents of) the cell each time earlier than you show your precise information. 😉
Initialization can also be dealt with by the system, nevertheless it’s value to say that in case you are working with Interface Builder, you must do your customization contained in the awakeFromNib technique, however in case you are utilizing code, init(body:) is your home.
import UIKit
class MyCell: UICollectionViewCell {
weak var textLabel: UILabel!
override init(body: CGRect) {
tremendous.init(body: body)
let textLabel = UILabel(body: .zero)
textLabel.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
contentView.addSubview(textLabel)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
textLabel.topAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: contentView.topAnchor
),
textLabel.bottomAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: contentView.bottomAnchor
),
textLabel.leadingAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: contentView.leadingAnchor
),
textLabel.trailingAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: contentView.trailingAnchor
),
])
self.textLabel = textLabel
contentView.backgroundColor = .lightGray
textLabel.textAlignment = .heart
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
tremendous.init(coder: aDecoder)
fatalError("Interface Builder just isn't supported!")
}
override func awakeFromNib() {
tremendous.awakeFromNib()
fatalError("Interface Builder just isn't supported!")
}
override func prepareForReuse() {
tremendous.prepareForReuse()
textLabel.textual content = nil
}
}
Subsequent we’ve to implement the view controller which is chargeable for managing the gathering view, we’re not utilizing IB so we’ve to create it manually by utilizing Auto Structure anchors – like for the textLabel within the cell – contained in the loadView technique. After the view hierarchy is able to rock, we additionally set the info supply and delegate plus register our cell class for additional reuse. Word that that is executed routinely by the system in case you are utilizing IB, however if you happen to desire code you must do it by calling the right registration technique. You may register each nibs and courses.
import UIKit
class ViewController: UIViewController {
weak var collectionView: UICollectionView!
override func loadView() {
tremendous.loadView()
let collectionView = UICollectionView(
body: .zero,
collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewFlowLayout()
)
collectionView.translatesAutoresizingMaskIntoConstraints = false
view.addSubview(collectionView)
NSLayoutConstraint.activate([
collectionView.topAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: view.topAnchor
),
collectionView.bottomAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: view.bottomAnchor
),
collectionView.leadingAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: view.leadingAnchor
),
collectionView.trailingAnchor.constraint(
equalTo: view.trailingAnchor
),
])
self.collectionView = collectionView
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
tremendous.viewDidLoad()
collectionView.backgroundColor = .white
collectionView.dataSource = self
collectionView.delegate = self
collectionView.register(
MyCell.self,
forCellWithReuseIdentifier: "MyCell"
)
}
}
extension ViewController: UICollectionViewDataSource {
func numberOfSections(
in collectionView: UICollectionView
) -> Int {
1
}
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
numberOfItemsInSection part: Int
) -> Int {
10
}
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
cellForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath
) -> UICollectionViewCell {
let cell = collectionView.dequeueReusableCell(
withReuseIdentifier: "MyCell",
for: indexPath
) as! MyCell
cell.textLabel.textual content = String(indexPath.row + 1)
return cell
}
}
extension ViewController: UICollectionViewDelegate {
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
didSelectItemAt indexPath: IndexPath
) {
print(indexPath.row + 1)
}
}
extension ViewController: UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout {
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
structure collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout,
sizeForItemAt indexPath: IndexPath
) -> CGSize {
.init(
width: collectionView.bounds.measurement.width - 16,
peak: 120
)
}
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
structure collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout,
minimumLineSpacingForSectionAt part: Int
) -> CGFloat {
8
}
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
structure collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout,
minimumInteritemSpacingForSectionAt part: Int
) -> CGFloat {
0
}
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
structure collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout,
insetForSectionAt part: Int
) -> UIEdgeInsets {
.init(high: 8, left: 8, backside: 8, proper: 8)
}
}
This time you must pay some consideration on the move structure delegate strategies. You should utilize these strategies to offer metrics for the structure system. The move structure will show all of the cells based mostly on these numbers and sizes. sizeForItemAt is chargeable for the cell measurement, minimumInteritemSpacingForSectionAt is the horizontal padding, minimumLineSpacingForSectionAt is the vertical padding, and insetForSectionAt is for the margin of the gathering view part.
So on this part I’m going to each use storyboards, nibs and a few Swift code. That is my regular method for a couple of causes. Though I really like making constraints from code, most individuals desire visible editors, so all of the cells are created inside nibs. Why nibs? As a result of if in case you have a number of assortment views that is “nearly” the one good option to share cells between them.
You may create part footers precisely the identical manner as you do headers, in order that’s why this time I’m solely going to give attention to headers, as a result of actually you solely have to alter one phrase so as to use footers. ⚽️
You simply must create two xib information, one for the cell and one for the header. Please observe that you could possibly use the very same assortment view cell to show content material within the part header, however this can be a demo so let’s simply go together with two distinct objects. You don’t even must set the reuse identifier from IB, as a result of we’ve to register our reusable views contained in the supply code, so simply set the cell class and join your retailers.
Cell and supplementary aspect registration is barely completely different for nibs.
let cellNib = UINib(nibName: "Cell", bundle: nil)
self.collectionView.register(
cellNib,
forCellWithReuseIdentifier: "Cell"
)
let sectionNib = UINib(nibName: "Part", bundle: nil)
self.collectionView.register(
sectionNib,
forSupplementaryViewOfKind: UICollectionView.elementKindSectionHeader,
withReuseIdentifier: "Part"
)
Implementing the info supply for the part header appears to be like like this.
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
viewForSupplementaryElementOfKind variety: String,
at indexPath: IndexPath
) -> UICollectionReusableView {
guard variety == UICollectionView.elementKindSectionHeader else {
return UICollectionReusableView()
}
let view = collectionView.dequeueReusableSupplementaryView(
ofKind: variety,
withReuseIdentifier: "Part",
for: indexPath
) as! Part
view.textLabel.textual content = String(indexPath.part + 1)
return view
}
Offering the scale for the move structure delegate can also be fairly easy, nevertheless generally I don’t actually get the naming conventions by Apple. As soon as you must swap a form, and the opposite time there are precise strategies for particular varieties. 🤷♂️
func collectionView(
_ collectionView: UICollectionView,
structure collectionViewLayout: UICollectionViewLayout,
referenceSizeForHeaderInSection part: Int
) -> CGSize {
.init(
width: collectionView.bounds.measurement.width,
peak: 64
)
}
Ranging from iOS9 part headers and footers will be pinned to the highest or backside of the seen bounds of the gathering view.
if let flowLayout = self.collectionView.collectionViewLayout as? UICollectionViewFlowLayout {
flowLayout.sectionHeadersPinToVisibleBounds = true
}
That’s it, now you know the way to construct fundamental layouts with assortment view.
What about complicated instances, like utilizing a number of sorts of cells in the identical assortment view? Issues can get fairly messy with index paths, in order that’s why I re-invented one thing higher based mostly on a method methods to construct superior person interfaces with assortment views showcased by Apple again at WWDC 2014.
My CollectionView based mostly UI framework
Now the fundamentals, so why don’t we get straight to the purpose? I’ll present you my greatest observe of constructing nice person interfaces through the use of my MVVM structure based mostly CollectionView micro framework.
CollectionView + ViewModel sample = ❤️ .
I’ll clarify the parts actual fast and after that you just’ll discover ways to use them to construct up the Apple music-ish structure that I used to be speaking about to start with. 🎶
Grid system
The primary drawback with assortment views is the scale calculation. You need to present the scale (width & peak) for every cell inside your assortment view.
- if all the pieces has a set measurement inside your assortment view, you may simply set the scale properties on the move structure itself
- if you happen to want dynamic sizes per merchandise, you may implement the move structure delegate aka. UICollectionViewDelegateFlowLayout (why is the delegate phrase in the midst of the title???) and return the precise sizes for the structure system
- if you happen to want much more management you may create a brand new structure subclass derived from CollectionView(Circulation)Structure and do all the scale calculations there
Thats good, however nonetheless you must mess with index paths, trait collections, frames and lots of extra so as to have a easy 2, 4, n column structure that adapts on each system. That is the explanation why I’ve created a extremely fundamental grid system for measurement calculation. With my grid class you may simply set the variety of columns and get again the scale for x quantity of columns, “identical to” in net based mostly css grid techniques. 🕸
Cell reuse
Registering and reusing cells ought to and will be automated in a sort secure method. You simply need to use the cell, and also you shouldn’t care about reuse identifiers and cell registration in any respect. I’ve made a pair helper strategies so as to make the progress extra nice. Reuse identifiers are derived from the title of the cell courses, so that you dont’t have to fret about anymore. It is a observe that a lot of the builders use.
View mannequin
view mannequin = cell (view) + information (mannequin)
Filling up “template” cell with actual information ought to be the duty of a view mannequin. That is the place MVVM comes into play. I’ve made a generic base view mannequin class, that you must subclass. With the assistance of a protocol, you should utilize numerous cells in a single assortment view with out going loopy of the row & part calculations and you may give attention to one easy job: connecting view with fashions. 😛
Part
part = header + footer + cells
I’m attempting to emphasise that you just don’t need to mess with index paths, you simply need to put your information collectively and that’s it. Up to now I’ve struggled greater than sufficient with “pointless index path math”, so I’ve made the part object as a easy container to wrap headers, footers and all of the objects inside the part. The consequence? Generic information supply class that can be utilized with a number of cells with none row or part index calculations. 👏👏👏
Supply
So so as to make all of the issues I’ve talked about above work, I wanted to implement the gathering view delegate, information supply, and move structure delegate strategies. That’s how my supply class was born. Every thing is carried out right here, and I’m utilizing sections, view fashions the grid system to construct up assortment views. However hey, sufficient from this idea, let’s see it in observe. 👓
CollectionView framework instance software
The right way to make a any record or grid structure problem free? Properly, as a primary step simply add my CollectionView framework as a dependency. Don’t fear you gained’t remorse it, plus it helps Xcode 11 already, so you should utilize the Swift Package deal Supervisor, straight from the file menu to combine this bundle.
Tip: simply add the @_exported import CollectionView line within the AppDelegate file, then you definately I don’t have to fret about importing the framework file-by-file.
Step 1. Make the cell.
This step is similar with the common setup, besides that your cell must be a subclass of my Cell class. Add your personal cell and do all the pieces as you’ll do usually.
import UIKit
class AlbumCell: Cell {
@IBOutlet weak var textLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var detailTextLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var imageView: UIImageView!
override func awakeFromNib() {
tremendous.awakeFromNib()
self.textLabel.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 12, weight: .daring)
self.textLabel.textColor = .black
self.detailTextLabel.font = UIFont.systemFont(ofSize: 12, weight: .daring)
self.detailTextLabel.textColor = .darkGray
self.imageView.layer.cornerRadius = 8
self.imageView.layer.masksToBounds = true
}
override func reset() {
tremendous.reset()
self.textLabel.textual content = nil
self.detailTextLabel.textual content = nil
self.imageView.picture = nil
}
}
Step 2. Make a mannequin
Simply decide a mannequin object. It may be something, however my method is to make a brand new struct or class with a Mannequin suffix. This fashion I do know that fashions are referencing the gathering view fashions inside my reusable parts folder.
import Basis
struct AlbumModel {
let artist: String
let title: String
let picture: String
}
Step 3. Make the view mannequin.
Now as an alternative of configuring the cell contained in the delegate, or in a configure technique someplace, let’s make an actual view mannequin for the cell & the info mannequin that’s going to be represented through the view.
import UIKit
class AlbumViewModel: ViewModel<AlbumCell, AlbumModel> {
override func updateView() {
self.view?.textLabel.textual content = self.mannequin.artist
self.view?.detailTextLabel.textual content = self.mannequin.title
self.view?.imageView.picture = UIImage(named: self.mannequin.picture)
}
override func measurement(grid: Grid) -> CGSize {
if
(self.collectionView.traitCollection.userInterfaceIdiom == .cellphone &&
self.collectionView.traitCollection.verticalSizeClass == .compact) ||
self.collectionView?.traitCollection.userInterfaceIdiom == .pad
{
return grid.measurement(
for: self.collectionView,
ratio: 1.2,
objects: grid.columns / 4,
gaps: grid.columns - 1
)
}
if grid.columns == 1 {
return grid.measurement(for: self.collectionView, ratio: 1.1)
}
return grid.measurement(
for: self.collectionView,
ratio: 1.2,
objects: grid.columns / 2,
gaps: grid.columns - 1
)
}
}
Step 4. Setup your information supply.
Now, use your actual information and populate your assortment view utilizing the view fashions.
let grid = Grid(columns: 1, margin: UIEdgeInsets(all: 8))
self.collectionView.supply = .init(grid: grid, [
[
HeaderViewModel(.init(title: "Albums"))
AlbumViewModel(self.album)
],
])
self.collectionView.reloadData()
Step 5. 🍺🤘🏻🎸
Congratulations you’re executed together with your first assortment view. With just some strains of code you’ve a ROCK SOLID code that can make it easier to out in a lot of the conditions! 😎
That is simply the tip of the iceberg! 🚢
What if we make a cell that accommodates a group view and we use the identical technique like above? A set view containing a group view… UICollectionViewception!!! 😂
It’s utterly attainable, and very easy to do, the info that feeds the view mannequin will probably be a group view supply object, and also you’re executed. Easy, magical and tremendous good to implement, additionally included within the instance app.
Sections with artists & round pictures
A number of sections? No drawback, round pictures? That’s additionally a bit of cake, if you happen to had learn my earlier tutorial about round assortment view cells, you’ll know methods to do it, however please take a look at the supply code from GitLab and see it for your self in motion.
Callbacks and actions
Person occasions will be dealt with very straightforward, as a result of view fashions can have delegates or callback blocks, it solely is dependent upon you which ones one you like. The instance accommodates an onSelect handler, which is tremendous good and built-in to the framework. 😎
Dynamic cell sizing re-imagined
I additionally had a tutorial about assortment view self sizing cell assist, however to be sincere I’m not a giant fan of Apple’s official technique. After I’ve made the grid system and began utilizing view fashions, it was less difficult to calculate cell heights on my own, with about 2 strains of additional code. I consider that’s value it, as a result of self sizing cells are a bit buggy if it involves auto rotation.
Rotation assist, adaptivity
Don’t fear about that an excessive amount of, you may merely change the grid or examine trait collections contained in the view mannequin if you’d like. I’d say nearly all the pieces will be executed proper out of the field. My assortment view micro framework is only a light-weight wrapper across the official assortment view APIs. That’s the fantastic thing about it, be happy to do no matter you need and use it in a manner that YOU personally desire. 📦
Now go, seize the pattern code and take heed to some steel! 🤘🏻
What if I informed you… yet one more factor: SwiftUI
These are some authentic quotes of mine again from April, 2018:
In the event you like this technique that’s cool, however what if I informed you that there’s extra? Do you need to use the identical sample in every single place? I imply on iOS, tvOS, macOS and even watchOS. Accomplished deal! I’ve created all the pieces contained in the CoreKit framework. UITableViews, WKInterfaceTables are supported as effectively.
Properly, I’m a visionary, however SwiftUI was late 1 yr, it arrived in 2019:
I actually consider that Apple this yr will method the subsequent era UIKit / AppKit / UXKit frameworks (written in Swift in fact) considerably like this. I’m not speaking in regards to the view mannequin sample, however about the identical API on each platform pondering. Anyway, who is aware of this for sue, we’ll see… #wwdc18 🤔
If somebody from Apple reads this, please clarify me why the hell is SwiftUI nonetheless an abstraction layer above UIKit/ AppKit as an alternative of a refactored AppleKit UI framework that lastly unifies each single API? For actual, why? Nonetheless don’t get it. 🤷♂️
Anyway, we’re stepping into to the identical route guys, year-by-year I delete increasingly self-written “Third-party” code, so that you’re doing nice progress there! 🍎